Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by the darkening of certain areas of the skin due to an excess production of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. This condition can manifest as dark spots, patches, or an overall increase in skin tone in specific regions. While hyperpigmentation itself is not harmful and does not pose any health risks, it can lead to significant psychological distress for those affected, as it often alters the appearance of the skin in ways that some may find undesirable.
The condition can affect individuals of all skin types and ethnicities, although it may be more pronounced in those with darker skin tones. Hyperpigmentation can occur anywhere on the body but is most commonly seen on sun-exposed areas such as the face, hands, and arms. The visibility of these darkened patches can vary widely, ranging from small freckles to larger areas that cover significant portions of the skin.
Understanding hyperpigmentation is essential for those seeking to manage or treat this condition effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by dark patches or spots on the skin.
- Causes of hyperpigmentation include sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and skin injuries.
- Types of hyperpigmentation include melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and sun-induced hyperpigmentation.
- Factors that contribute to hyperpigmentation include genetics, skin type, and certain medications.
- Treatment options for hyperpigmentation include topical creams, chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
The causes of hyperpigmentation are multifaceted and can be attributed to a variety of factors. One of the primary triggers is sun exposure. Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun stimulate melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin.
Prolonged exposure to sunlight can lead to an overproduction of melanin, resulting in sunspots or age spots, particularly in individuals who do not use adequate sun protection. This type of hyperpigmentation is often seen in areas that are frequently exposed to sunlight. Hormonal changes also play a significant role in the development of hyperpigmentation.
Conditions such as melasma, which is often referred to as “the mask of pregnancy,” can occur due to fluctuations in hormones during pregnancy or as a result of taking oral contraceptives. Melasma typically presents as brown or gray-brown patches on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. Additionally, certain medications can induce hyperpigmentation as a side effect, further complicating the landscape of this condition.
Types of Hyperpigmentation

Hyperpigmentation can be categorized into several distinct types, each with its own underlying causes and characteristics. One of the most common forms is solar lentigines, often referred to as age spots or liver spots. These are flat, brown spots that develop on sun-exposed areas of the skin due to cumulative sun damage over time.
They are typically harmless but can be cosmetically concerning for many individuals. Another prevalent type is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), which occurs following an injury or inflammation to the skin. This can result from acne, eczema, psoriasis, or even minor cuts and scrapes.
The skin darkens in response to inflammation as part of the healing process, leading to darkened patches that may persist long after the initial injury has healed. PIH is particularly common among individuals with darker skin tones due to increased melanin production in response to inflammation. Melasma is another significant type of hyperpigmentation that primarily affects women and is often associated with hormonal changes.
It typically appears as symmetrical brown patches on the face and is exacerbated by sun exposure. Understanding these different types of hyperpigmentation is crucial for determining appropriate treatment strategies.
Factors that Contribute to Hyperpigmentation
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| UV Exposure | Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can trigger melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation. |
| Hormonal Changes | Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can contribute to the development of hyperpigmentation. |
| Inflammation | Chronic inflammation, often caused by conditions like acne or eczema, can stimulate melanocytes and result in hyperpigmentation. |
| Genetics | Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing hyperpigmentation due to variations in their melanin production. |
| Medications | Certain medications, such as some antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs, can increase the skin’s sensitivity to UV radiation and lead to hyperpigmentation. |
Several factors contribute to the development and exacerbation of hyperpigmentation beyond just sun exposure and hormonal changes. Genetics plays a critical role; individuals with a family history of hyperpigmentation may be more predisposed to developing similar conditions. Certain ethnic groups are also more susceptible due to genetic variations in melanin production.
Environmental factors can also influence hyperpigmentation. Pollution and exposure to environmental toxins can lead to oxidative stress in the skin, which may trigger an inflammatory response and subsequent melanin overproduction. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as smoking and poor diet can negatively impact skin health and contribute to pigmentation issues.
Age is another significant factor; as individuals grow older, their skin undergoes various changes that can lead to increased pigmentation. The cumulative effects of sun exposure over the years often manifest as age spots or other forms of hyperpigmentation. Understanding these contributing factors is essential for both prevention and treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Hyperpigmentation
When it comes to treating hyperpigmentation, a multifaceted approach is often necessary. The first step in any treatment plan should involve identifying the underlying cause of the pigmentation issue. For instance, if sun exposure is a primary factor, implementing rigorous sun protection measures becomes paramount.
This includes using broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours. Topical treatments are commonly employed to address hyperpigmentation directly. Ingredients such as hydroquinone, retinoids, vitamin C, and azelaic acid have been shown to be effective in lightening dark spots and evening out skin tone.
Hydroquinone works by inhibiting melanin production, while retinoids promote cell turnover and help fade pigmentation over time. Vitamin C serves as an antioxidant that not only brightens the skin but also protects it from further damage. In more severe cases or when topical treatments fail to yield satisfactory results, individuals may consider professional interventions such as chemical peels or laser therapy.
These procedures can provide more immediate results by targeting deeper layers of the skin where pigmentation resides.
Over-the-Counter Products for Hyperpigmentation
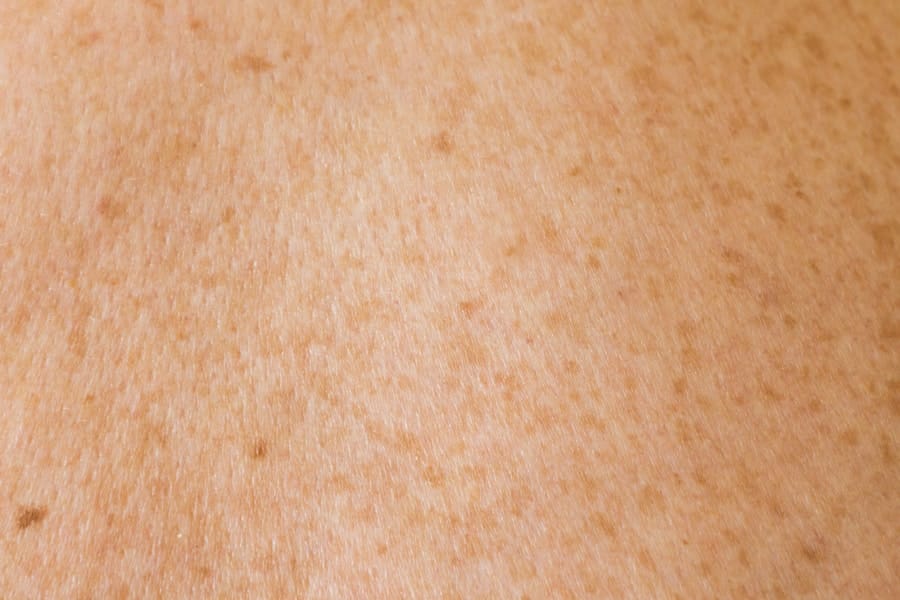
Alternative Ingredients to Hydroquinone
Kojic acid is another effective ingredient found in various skincare products designed for hyperpigmentation treatment. Derived from fungi, kojic acid works by inhibiting melanin production and has been shown to lighten dark spots effectively. Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, has also gained popularity due to its ability to reduce pigmentation while improving overall skin texture and barrier function.
Exfoliating with Alpha Hydroxy Acids
Additionally, products containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid can help exfoliate the skin’s surface and promote cell turnover, leading to a brighter complexion over time.
Selecting the Right Product
When selecting over-the-counter products for hyperpigmentation, it’s essential for consumers to look for clinically tested formulations that contain these active ingredients at effective concentrations.
Professional Treatments for Hyperpigmentation
For individuals seeking more aggressive treatment options for hyperpigmentation, professional dermatological procedures offer promising results. Chemical peels are one such option; they involve applying a chemical solution to the skin that exfoliates the outer layers and promotes new skin growth. Depending on the strength of the peel used—ranging from superficial to deep—patients may experience varying degrees of downtime but often see significant improvements in pigmentation after just one or two sessions.
Laser therapy has also emerged as a highly effective treatment modality for hyperpigmentation. Various types of lasers target melanin directly within the skin without damaging surrounding tissues. For instance, fractional lasers create micro-injuries in the skin that stimulate collagen production while simultaneously breaking down excess melanin deposits.
This dual action not only helps reduce pigmentation but also improves overall skin texture. Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy is another professional option that utilizes broad-spectrum light to target pigmented lesions effectively. IPL treatments are non-invasive and typically require multiple sessions for optimal results but can significantly reduce the appearance of dark spots without significant downtime.
Preventing Hyperpigmentation
Preventing hyperpigmentation requires a proactive approach focused on protecting the skin from known triggers while promoting overall skin health. One of the most effective preventive measures is diligent sun protection. Regularly applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher is crucial for preventing UV-induced pigmentation changes.
It’s important to reapply sunscreen every two hours when outdoors and immediately after swimming or sweating. In addition to sun protection, adopting a comprehensive skincare routine that includes antioxidants can help mitigate oxidative stress on the skin caused by environmental factors such as pollution and UV exposure. Incorporating products with vitamin C or other antioxidants can provide an additional layer of defense against pigmentation issues.
Furthermore, individuals should be cautious about aggressive skincare practices that could lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. This includes avoiding picking at acne lesions or using harsh exfoliants that may irritate the skin. Instead, opting for gentle exfoliation methods and maintaining a consistent skincare regimen tailored to one’s specific skin type can help maintain an even complexion while minimizing the risk of developing hyperpigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, and inflammation. One way to help reduce hyperpigmentation is by using products containing alpha arbutin, a natural skin-lightening ingredient. For more information on the benefits and side effects of alpha arbutin, check out this article on Alpha Palm Vitamin Benefits, Dosage, and Side Effects for Optimal Health. This article provides valuable insights into how alpha arbutin can help improve the appearance of hyperpigmentation and achieve a more even skin tone.
FAQs
What is hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that causes dark patches or spots to form on the skin. It occurs when the skin produces an excess of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
What causes hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by a variety of factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes (such as pregnancy or birth control pills), skin injuries or inflammation, and certain medications.
What are the different types of hyperpigmentation?
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, including melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and sun-induced hyperpigmentation (also known as sun spots or age spots).
How is hyperpigmentation treated?
Treatment for hyperpigmentation may include topical creams or serums containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C, chemical peels, laser therapy, or microdermabrasion. Sun protection is also important in preventing and treating hyperpigmentation.
Can hyperpigmentation be prevented?
Preventing hyperpigmentation involves protecting the skin from sun exposure by using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade. It’s also important to avoid picking at or irritating the skin, and to manage any underlying conditions that may contribute to hyperpigmentation.
