“The male reproductive system is a fascinating and complex network of organs that play a vital role in the perpetuation of life. From the highly specialized sperm cells to the intricate hormonal balance, there is much more to this system than meets the eye. In this article, we will into the intricacies of the male reproductive system, shedding light on its functions and exploring the wonders that lie within.”
The Journey Begins: An Introduction to the Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system is a marvel of biology, working in tandem to ensure the continuation of the human species. Comprised of various organs and structures, this interconnected network operates with breathtaking precision. Let’s embark on a journey through the male reproductive system and unravel its well-kept secrets.
The Testes: Orchestrators of Life
The testes, or testicles, are the primary organ within the male reproductive system. These oval-shaped wonders are responsible for the production of sperm and the secretion of testosterone, a crucial male sex hormone. When puberty strikes, the testes come alive, releasing millions of sperm cells daily, each carrying the potential to fertilize an egg.
The Epididymis: A Secretive Chamber
Nested within each testicle lies the epididymis, a tightly coiled tube that serves as a storage and maturation site for sperm. Spanning approximately 20 feet when unraveled, this enigmatic structure allows sperm cells to develop both their mobility and the ability to fertilize an egg. With time, these mature sperm cells make their way through the epididymis, awaiting their moment of opportunity.
The Vas Deferens: A Path to Journey
When the time comes for a sperm cell to embark on its adventure, it travels through the vas deferens. Functioning as a muscular tube, the vas deferens connects the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts. During ejaculation, muscular contractions propel the sperm cells forward, embarking them on their mission to participate in the miracle of life.
The Prostate Gland: A Guardian for the Sperm
The prostate gland, often referred to as the “guardian of the sperm,” is a mighty organ positioned beneath the bladder. This gland contributes to the nourishment and protection of sperm by secreting seminal fluid, a substance that provides the energy and resources needed for sperm cells to reach their destination.
The Seminal Vesicles: Nurturers of Life
The seminal vesicles, located near the prostate gland, contribute to the production of seminal fluid. These pouch-like structures secrete a nutrient-rich fluid that acts as a nurturing medium, aiding sperm cells in their quest to reach and fertilize an egg. Without the support of the seminal vesicles, the journey of the sperm would be considerably more challenging.
The Urethra: The Dual-Purpose Passageway
At the core of the male reproductive system lies the urethra, a multifunctional passageway responsible for both urine and seminal fluid transport. This marvel of adaptation ensures the coordination of bodily functions, allowing for the safe and controlled release of both waste and life-generating fluid.
The Penis: The Key to Reproduction
The male reproductive system culminates in the majestic organ known as the penis. Functioning both as a conduit for urine and a delivery mechanism for semen, the penis is a symbol of masculinity and plays a paramount role in reproduction. Through a magnificent interplay of vascular, neural, and muscular systems, this organ enables the transfer of sperm into the female reproductive tract.
Embracing Knowledge: The Importance of Understanding the Male Reproductive System
Understanding the male reproductive system goes beyond mere curiosity. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their sexual health. From the prevention and management of reproductive disorders to fertility planning, knowledge of this system is crucial for both men and their partners.
By shedding light on the male reproductive system, we ignite a spark of consciousness, fostering healthier habits, and encouraging open conversations. May this knowledge serve as a catalyst for appreciation and better overall well-being.
“Knowledge about the male reproductive system is like a compass, guiding us towards better sexual health and a deeper understanding of the miracles our bodies can create.”
Remember, gentlemen, you possess an intricate masterpiece within you. Understanding and appreciating the male reproductive system is the key to unlocking a world of discovery and appreciation for the incredible wonders of life.
- External Links:
FAQ
1. Does a male reproductive system have the tendency to skip a generation?
The male reproductive system does not exhibit a generational skipping pattern. Genetic traits related to reproductive organs and functions are inherited, but skipping a generation is not a characteristic of these traits. Variations in reproductive health can be influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
2. What are the latest developments in medications for addressing prostate function in the male reproductive system?
Recent developments in medications for prostate function include drugs targeting conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are commonly prescribed to manage BPH symptoms. Additionally, ongoing research explores novel medications with fewer side effects for enhanced prostate health.
3. Can you share a comprehensive male reproductive system diagram highlighting its parts and functions?
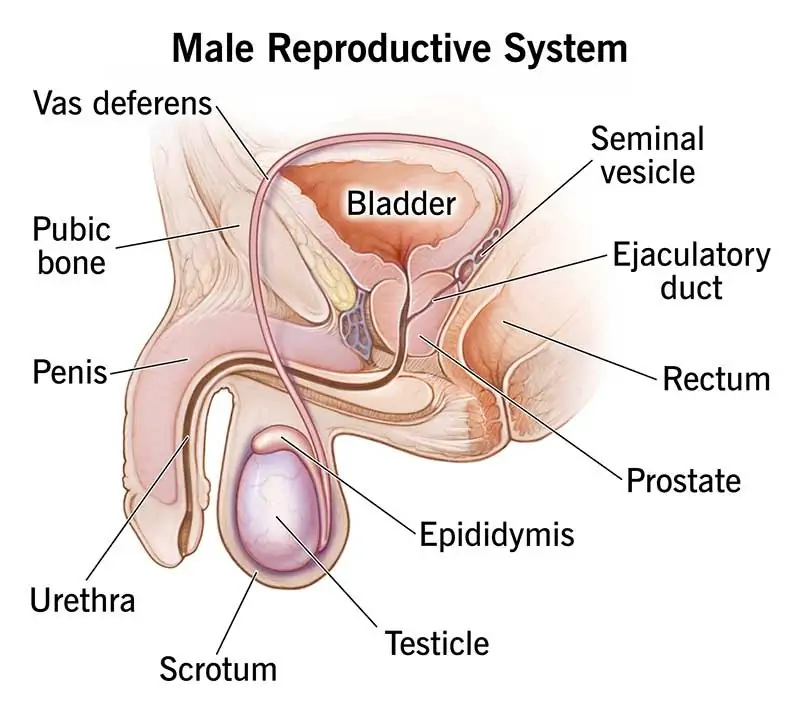
4. How is the male reproductive organ structured, and what role does it play in the reproductive process?
The male reproductive organ, the penis, is composed of erectile tissue and serves multiple functions. During sexual arousal, it becomes erect, facilitating penetration during intercourse. It also plays a crucial role in the release of semen during ejaculation, aiding in the transportation of sperm into the female reproductive tract for fertilization.
5. What are the 10 parts of the male reproductive system, and how do they contribute to reproductive functions?
The male reproductive system comprises several parts, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and more. Each part contributes uniquely to reproductive functions, such as sperm production, storage, and transportation, as well as the secretion of fluids that form semen.
6. Explain the significance of the 11 parts of the male reproductive system in the overall reproductive process.
The male reproductive system consists of critical components, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and others. These parts collectively contribute to the reproductive process. The testes produce sperm, while the epididymis stores and matures them. The vas deferens transports sperm to the urethra. Accessory glands like the prostate and seminal vesicles produce seminal fluid, supporting sperm viability and motility during ejaculation.
7. How does the male anatomy influence and interact with the workings of the reproductive system?
The male anatomy, especially the reproductive organs, plays a fundamental role in the reproductive system’s function. Hormonal signals regulate sperm production in the testes. The interplay of the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and accessory glands ensures the production, maturation, and transportation of sperm for fertilization. The coordination of these structures is crucial for successful reproduction.
8. What are the three main parts of the male reproductive system, and how do they collaborate for reproduction?
The three main parts of the male reproductive system are the testes, vas deferens, and penis. The testes produce sperm, the vas deferens transports sperm from the testes to the urethra, and the penis facilitates the release of sperm during ejaculation. Collaboration among these structures ensures the delivery of sperm to the female reproductive tract for fertilization.
9. Can you provide a detailed 3D representation of the male reproductive system, illustrating its structures?
Unfortunately, I can’t provide visual content, but there are various online resources and medical textbooks that offer detailed 3D representations of the male reproductive system. If you have specific questions about the structures, I can describe them in detail.
10. Describe the roles of the 5 main parts of the male reproductive system in the reproductive process.
The five main parts of the male reproductive system—testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles—play distinct roles in reproduction. The testes produce sperm, the epididymis stores and matures sperm, the vas deferens transports sperm, and the prostate gland and seminal vesicles contribute seminal fluid. Collectively, these structures facilitate the production, storage, and transportation of sperm for successful fertilization.
11. What are the 7 parts of the male reproductive system, and how do they collectively contribute to reproduction?
The male reproductive system comprises several key parts, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, penis, and scrotum. Each part plays a crucial role in reproduction:
- Testes: These are the primary reproductive organs responsible for producing sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis: Sperm produced in the testes mature and are stored in the epididymis, where they gain motility.
- Vas Deferens: This duct transports mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
- Prostate Gland: Produces a significant portion of seminal fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
- Seminal Vesicles: These glands contribute additional fluids to semen, enhancing sperm motility and viability.
- Penis: The male organ that facilitates the release of semen into the female reproductive tract during ejaculation.
- Scrotum: This pouch-like structure houses the testes outside the body, maintaining a lower temperature necessary for sperm production.
Collectively, these parts work in harmony to produce, mature, store, and transport sperm, ensuring the successful delivery of sperm to the female reproductive system for fertilization.
12. Explain the functions of the 8 parts of the male reproductive system and their significance.
The male reproductive system consists of several essential parts, each with distinct functions:
- Testes: Primarily responsible for sperm production and the secretion of testosterone, a key male sex hormone.
- Epididymis: Serves as a storage site for mature sperm and facilitates their maturation.
- Vas Deferens: Transports mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
- Prostate Gland: Produces seminal fluid, containing nutrients and enzymes that support sperm viability.
- Seminal Vesicles: Contribute additional fluids to semen, enhancing sperm motility and providing energy.
- Penis: Facilitates the release of semen into the female reproductive tract during ejaculation.
- Scrotum: Houses and protects the testes, maintaining a lower temperature for optimal sperm production.
- Urethra: Serves a dual purpose by carrying urine from the bladder and transporting semen during ejaculation.
The significance lies in the coordinated function of these parts, ensuring the production, maturation, and transportation of sperm for successful reproduction.
13. How is the male reproductive system composed of 9 organs, and what functions do they serve in reproduction?
The male reproductive system is composed of the following nine organs:
- Testes (2): Produce sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis (2): Stores and matures sperm.
- Vas Deferens (2): Transports mature sperm to the urethra.
- Prostate Gland (1): Produces seminal fluid to support sperm.
- Seminal Vesicles (2): Contribute fluids to semen, enhancing sperm motility.
- Penis (1): Facilitates the release of semen during ejaculation.
- Scrotum (1): Protects and regulates the temperature of the testes.
- Urethra (1): Transports semen and urine.
These organs collectively contribute to the process of reproduction by producing, maturing, storing, and transporting sperm, as well as providing essential fluids for semen.
14. Provide insights into the anatomical diagram of the male reproductive system, emphasizing structures and relationships.

The testes are housed in the scrotum, with the epididymis connected to each testis. The vas deferens extends from the epididymis, converging with seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct. This duct travels through the prostate gland, ultimately connecting to the urethra within the penis. Understanding these relationships is crucial for comprehending the sequential steps of sperm production, maturation, and ejaculation.
15. Could you elaborate on the anatomy and physiology of the male and female reproductive systems, highlighting the distinctions between them?
The male and female reproductive systems have distinct anatomies and functions. In males, the testes produce sperm and testosterone, while in females, the ovaries produce eggs and estrogen/progesterone. The male reproductive system includes structures like the epididymis and prostate gland, absent in females. Females have a uterus, where fertilized eggs implant and develop into a fetus, a structure not present in males. The female system undergoes menstrual cycles, while males continuously produce sperm. These distinctions highlight the specialized roles each system plays in reproduction.